- Home
- A-Z Catalogue
- Products
- Valves
- Cetop
- Manual Directional Valves
- Proportional Valves
- Poppet Valves
- High-Speed Linear Servo Valves
- All High-Speed Linear Servo Valves
- Cetop 10 (NG32) Two Stage Type High Speed Linear Servo Valves – LSVHG-10
- Cetop 10 (NG32) Two Stage Type High Speed Linear Servo Valves – LSVHG-10 (With Fail-Safe)
- Cetop 8 (NG25) Two Stage Type High Speed Linear Servo Valves – LSVHG-06
- Cetop 8 (NG25) Two Stage Type High Speed Linear Servo Valves – LSVHG-06 (With Fail-Safe)
- Cetop 7 (NG16) Two Stage Type High Speed Linear Servo Valves – LSVHG-04
- Cetop 7 (NG16) Two Stage Type High Speed Linear Servo Valves – LSVHG-04 (With Fail-Safe)
- Cetop 5 (NG10) Direct Type High Speed Linear Servo Valves – LSVG-03
- Cetop 5 (NG10) OBE Type Direct Operated Linear Servo Valves – LSVG-03-EH
- Cetop 3 (NG6) OBE Type Direct Operated Linear Servo Valves – LSVG-01-EH
- Pumps
- Pressure control
- Flow Control Valves
- Pressure Control Valves
- All Pressure Control Valves
- Brake Valves
- Direct Relief Valve
- Low Noise Solenoid Controlled Relief Valves
- Low Noise Pilot Operated Relief Valves
- Pilot Operated Relief Valves
- Pressure reducing and relieving valves
- Pressure reducing and check valves
- Pressure control valves
- Remote Control Relief Valves
- Solenoid Controlled Relief Valves – BSG
- Solenoid Controlled Relief Valves – BST
- Unloading relief valves
- Check valves
- Environmental
- Valves
- Hydraulic Systems
- Power pack
- About Us
- Contact
- Blog
How to Choose the Right Directional Control Valve for Your Project
Choosing the right directional control valve for your project is a critical decision that can significantly impact the efficiency and performance of hydraulic systems. According to a recent report by the International Hydraulics Association, directional control valves represent approximately 30% of the total market share in hydraulic components, highlighting their importance in the industry. As industries continue to modernize and demand for efficient fluid control systems grows, understanding how to select the appropriate valve becomes paramount.
Industry experts like Dr. Emily Chen, a leading figure in fluid power technology, emphasize the importance of making informed choices when it comes to directional control valves: “The right valve can enhance system responsiveness and reduce energy consumption, making it an indispensable component of any hydraulic application.” With a wealth of options available, it is essential to consider factors such as flow rate, pressure ratings, and actuation method to ensure the selected valve meets the specific requirements of your project. This introduction sets the stage for exploring the various considerations and best practices for selecting directional control valves that align with your operational needs.

Table of Contents
[Hide]
Understanding Directional Control Valves: Key Concepts and Types
Directional control valves play a crucial role in hydraulic systems, determining the flow path of the fluid within the system. Understanding the types and functions of these valves is essential for selecting the right valve for any project. There are several key types of directional control valves, including spool valves, poppet valves, and rotary valves. Each type has distinct operational characteristics and is suitable for different applications. According to a recent industry report, spool valves are frequently used due to their reliability and versatility, accounting for approximately 50% of the market share in hydraulic applications.
When choosing a directional control valve, it is important to consider several factors, such as the number of positions, the number of ways, and the required flow rates. A dual-spool valve, for example, can control multiple actuators and is ideal for applications requiring precise control over multiple hydraulic functions. Moreover, the response time and pressure ratings should align with the demands of your system. The market research indicates a growing trend towards more sophisticated valves that integrate digital control for enhanced performance and energy efficiency.
Tips: Always assess the system's specifications before selecting a valve. Ensure to account for the maximum flow and pressure requirements, as well as the temperature and viscosity of the fluid. Additionally, consult with industry experts if unsure, as the right choice can significantly impact the efficiency and reliability of your hydraulic system.
How to Choose the Right Directional Control Valve for Your Project - Understanding Directional Control Valves: Key Concepts and Types
| Valve Type | Actuation Method | Pressure Rating (psi) | Flow Rate (GPM) | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4/2 Way Valve | Manual | 2500 | 20 | Cylinders |
| 3/2 Way Valve | Electric | 3000 | 25 | Plumbing |
| 4/3 Way Valve | Pneumatic | 4000 | 30 | Industrial Automation |
| Load Sensing Valve | Hydraulic | 5000 | 15 | Construction Equipment |
| Check Valve | Automatic | 2000 | 40 | Fluid Control |
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Directional Control Valve
When selecting a directional control valve for your project, several key factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance and compatibility with your system. Firstly, understanding the flow requirements is crucial. This includes the maximum flow rate and the hydraulic pressure specifications. Evaluating the application can help determine whether you need a two-position or multiple-position valve, depending on the number of operating states required for your machinery.
Another vital consideration is the valve’s construction material. It should be compatible with the type of fluid being handled, taking into account factors such as temperature and potential corrosiveness. Additionally, the valve's response time and operating mechanism—be it manual, electric, or pneumatic—can significantly affect the performance of your system. Assessing the environment where the valve will be used is important for ensuring its durability and reliability under the anticipated conditions, including exposure to dust, moisture, or extreme temperatures.
Technical Specifications: Flow Rate, Pressure Rating, and Port Sizes
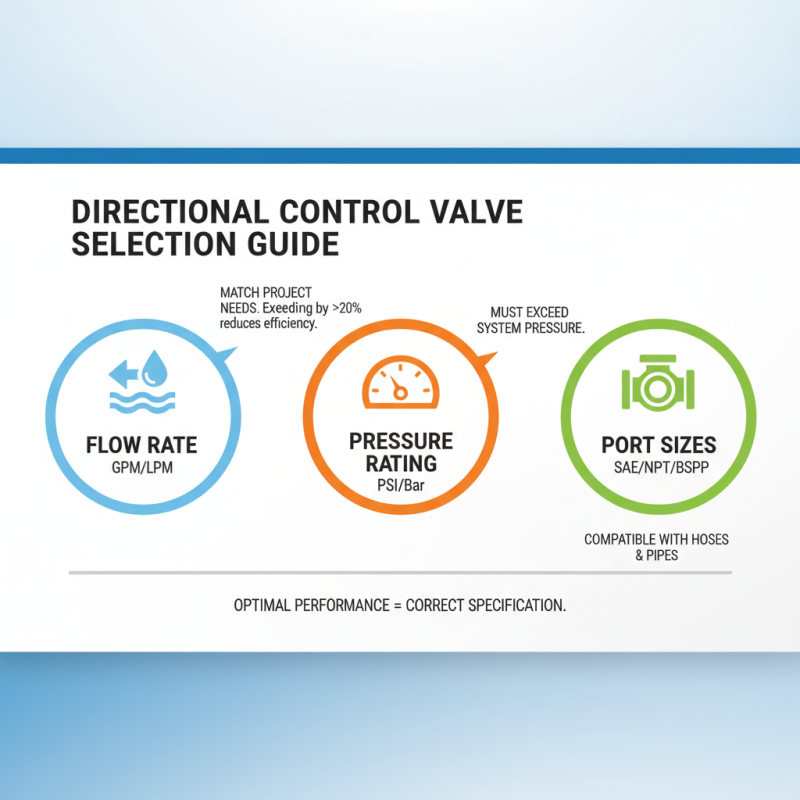
When selecting the right directional control valve for your project, key technical specifications must be meticulously considered, notably flow rate, pressure rating, and port sizes. The flow rate, typically measured in gallons per minute (GPM) or liters per minute (LPM), is crucial as it determines the amount of fluid that can pass through the valve under specific conditions. According to a report by the International Fluid Power Society, operational efficiency can decline significantly if the flow rate exceeds the valve's rated capacity by more than 20%. Thus, accurately matching the valve's flow specifications to the project's requirements is essential for optimal performance.
Pressure rating plays a pivotal role in ensuring the longevity and reliability of the directional control valve. For instance, valves with a higher pressure rating are better suited for high-pressure applications, which can reach up to 5000 psi or more in industrial scenarios. Data from Hydraulic Research and Technology highlights that using a valve with a lower pressure rating than required can lead to premature failure and costly downtime. Additionally, port sizes must align with the system's piping to prevent flow restrictions. The correct size not only enhances performance but also minimizes turbulence within the hydraulic system, further contributing to efficiency. In complex applications, it may be beneficial to conduct a flow analysis to ensure that the chosen valve optimally fits the project specifications.
Industry Standards: ISO and ANSI Guidelines for Control Valves
When selecting a directional control valve, adherence to industry standards is crucial for ensuring compatibility and performance. The two primary sets of guidelines that govern control valves are those established by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the American National Standards Institute (ANSI). According to a report from the Hydraulic Institute, adherence to ISO standards can enhance valve reliability, increase lifespan, and improve system efficiency by as much as 20%. ISO 5598, for example, provides essential terminology and classifications for valves and actuators, which helps in standardizing design processes across the industry.
ANSI standards also play a significant role in the selection process. They offer guidelines that enhance safety and ensure interoperability among different systems. The ANSI/ISA 75.05 standard outlines the specifications required for control valves, focusing on flow characteristics and performance assessments. A 2021 study by the Flow Control Institute highlighted that systems using ANSI-compliant valves experienced a 15% reduction in maintenance costs over five years, reflecting the long-term advantages of choosing valves designed according to established guidelines. By aligning with these standards, engineers can mitigate risks associated with valve performance and contribute to the seamless integration of their projects into existing systems.
Application Scenarios: Matching Valves to System Requirements
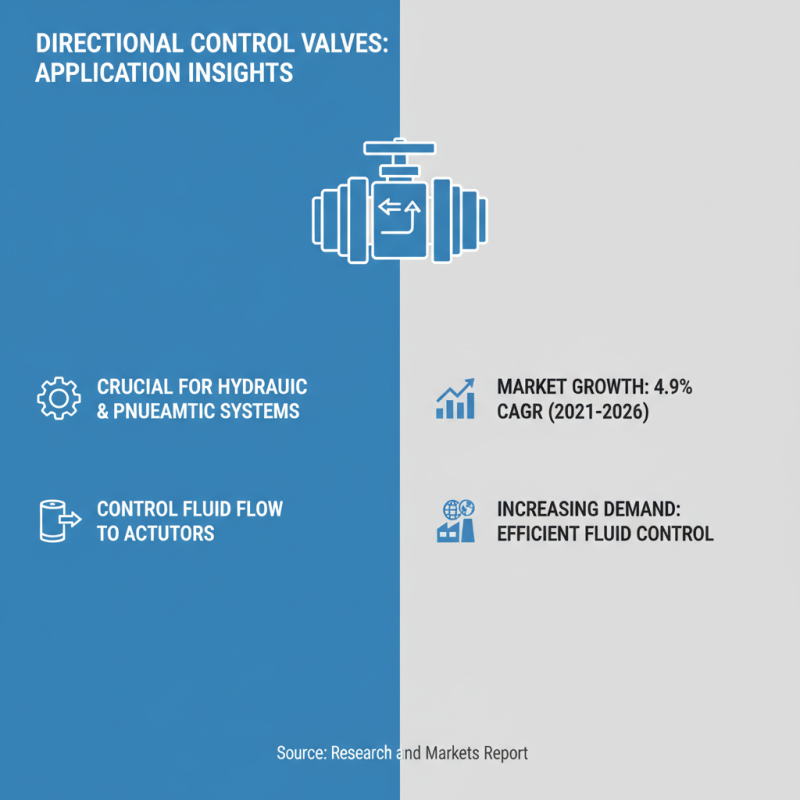
When selecting the appropriate directional control valve for a project, understanding the specific application scenarios is crucial to meeting system requirements. Directional control valves are integral components in hydraulic and pneumatic systems, controlling the flow of fluid to various actuators. According to a report by Research and Markets, the global market for directional control valves is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.9% from 2021 to 2026, emphasizing the increasing demand for efficient fluid control systems across multiple industries.
Choosing the right valve involves assessing the operating conditions such as pressure, flow rate, and environmental factors. For example, in automotive applications, a valve may need to operate efficiently under high pressure (up to 3000 psi) and varying temperatures while maintaining reliability. Conversely, in agricultural machinery, where exposure to dust and moisture is common, selecting a valve designed for harsh environments is essential to ensure longevity and reduce maintenance costs. Industry standards, such as ISO 4414, provide guidance on the performance requirements necessary to match valves to these diverse operational contexts.
Moreover, the configuration of the valve—such as 2-way, 3-way, or 4-way designs—must align with the specific actuation requirements of the system. A study published in the International Journal of Fluid Power indicates that improper valve selection can lead to up to 25% efficiency losses in hydraulic systems. Therefore, a thorough evaluation of the application scenario, paired with an understanding of the technical specifications of available valves, is vital for optimizing system performance and achieving project goals.
Related Posts
-

Exploring the Benefits of Advanced Hydraulic Directional Valves for Efficient Fluid Control
-
Understanding the Role of Hydraulic Valves in Modern Industrial Applications
-
Understanding the Importance of Hydraulic Pressure Control Valves in Modern Industrial Applications
-

The Essential Guide to Understanding Pressure Relief Valves: Safety and Function Explained
-

7 Essential Tips for Mastering Hydraulic Controls in Your Projects
-
2025 How to Choose the Best Yuken Valve for Your Hydraulic System












