- Home
- A-Z Catalogue
- Products
- Valves
- Cetop
- Manual Directional Valves
- Proportional Valves
- Poppet Valves
- High-Speed Linear Servo Valves
- All High-Speed Linear Servo Valves
- Cetop 10 (NG32) Two Stage Type High Speed Linear Servo Valves – LSVHG-10
- Cetop 10 (NG32) Two Stage Type High Speed Linear Servo Valves – LSVHG-10 (With Fail-Safe)
- Cetop 8 (NG25) Two Stage Type High Speed Linear Servo Valves – LSVHG-06
- Cetop 8 (NG25) Two Stage Type High Speed Linear Servo Valves – LSVHG-06 (With Fail-Safe)
- Cetop 7 (NG16) Two Stage Type High Speed Linear Servo Valves – LSVHG-04
- Cetop 7 (NG16) Two Stage Type High Speed Linear Servo Valves – LSVHG-04 (With Fail-Safe)
- Cetop 5 (NG10) Direct Type High Speed Linear Servo Valves – LSVG-03
- Cetop 5 (NG10) OBE Type Direct Operated Linear Servo Valves – LSVG-03-EH
- Cetop 3 (NG6) OBE Type Direct Operated Linear Servo Valves – LSVG-01-EH
- Pumps
- Pressure control
- Flow Control Valves
- Pressure Control Valves
- All Pressure Control Valves
- Brake Valves
- Direct Relief Valve
- Low Noise Solenoid Controlled Relief Valves
- Low Noise Pilot Operated Relief Valves
- Pilot Operated Relief Valves
- Pressure reducing and relieving valves
- Pressure reducing and check valves
- Pressure control valves
- Remote Control Relief Valves
- Solenoid Controlled Relief Valves – BSG
- Solenoid Controlled Relief Valves – BST
- Unloading relief valves
- Check valves
- Environmental
- Valves
- Hydraulic Systems
- Power pack
- About Us
- Contact
- Blog
10 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Pressure Reducing Valve
In the world of plumbing and fluid control, the pressure reducing valve (PRV) is a crucial component that ensures safety and efficiency within systems. As industry expert John Smith, a renowned engineer with over 15 years of experience in hydraulic systems, aptly states, "Choosing the right pressure reducing valve is not just about performance but about ensuring the longevity and reliability of your entire plumbing system." This statement underscores the significance of making informed decisions in selecting a PRV that meets your specific needs.
Understanding the various factors at play when choosing a pressure reducing valve can significantly impact your system's performance. From inlet and outlet pressure settings to flow rates and materials, each decision can lead to substantial differences in operational efficiency. Whether for industrial applications or residential plumbing, the right PRV plays an essential role in protecting pipes, fixtures, and appliances from potential damage caused by excessive pressure.
In this guide, we present ten essential tips to aid you in selecting the perfect pressure reducing valve for your application. By following these tips, you will not only optimize your system's function but also enhance its durability, ensuring a reliable solution that stands the test of time.
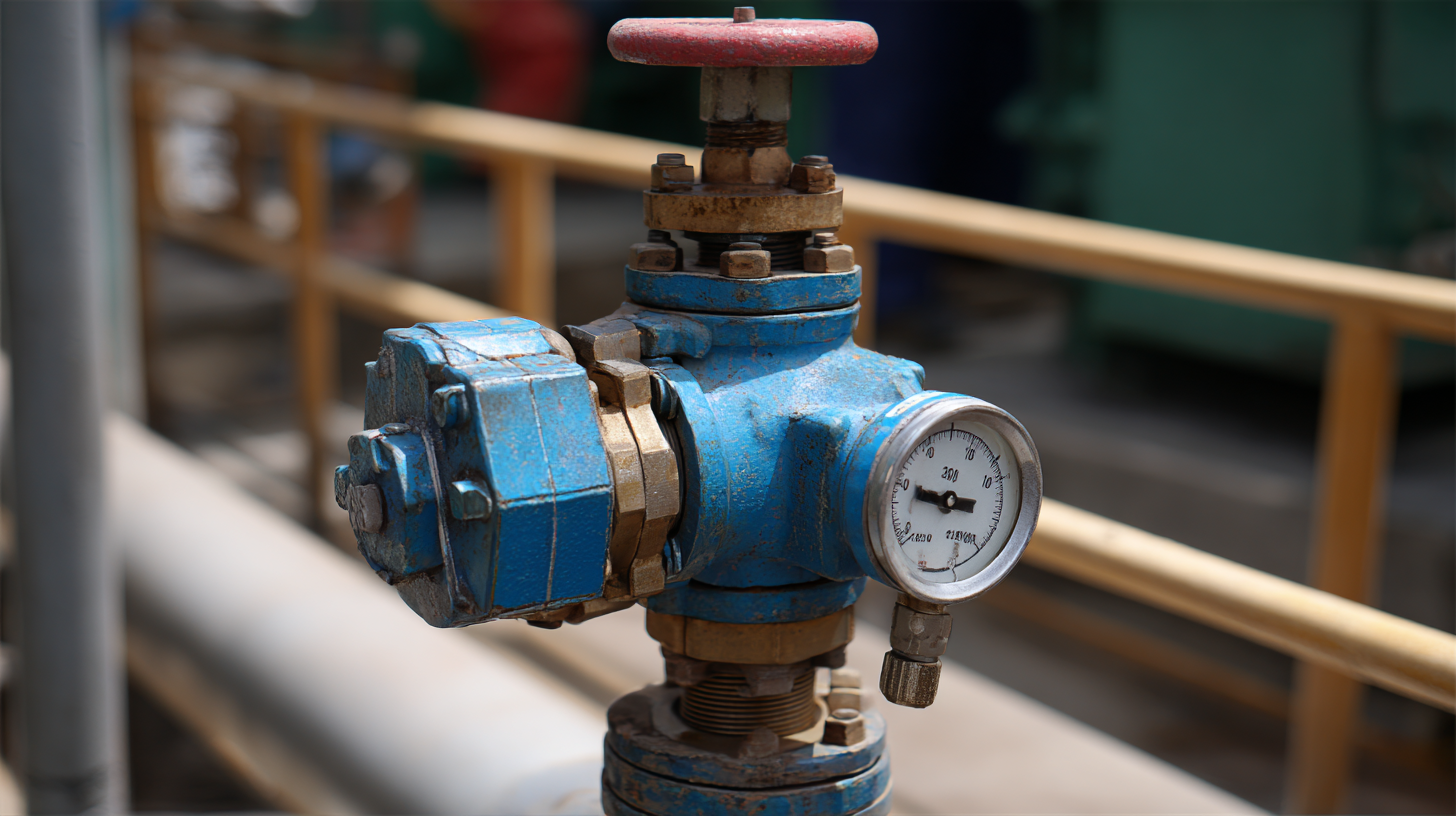

Table of Contents
[Hide]
Understanding Pressure Reducing Valve Basics for Optimal Application
When selecting a pressure reducing valve (PRV), it's imperative to grasp the fundamental principles that govern their operation. A pressure reducing valve is an essential component in many fluid systems, ensuring that downstream pressure remains consistently lower than the incoming pressure. This function is crucial for protecting sensitive equipment and maintaining system efficiency. Understanding parameters such as inlet and outlet pressure ratings, flow capacities, and valve types can significantly impact the effectiveness of the application.
The choice of the appropriate PRV also depends on the specific requirements of the system it will serve. Different applications may demand varying pressure settings and materials to withstand specific environmental conditions. For instance, a valve designed for potable water might differ significantly from one used in industrial processes. Familiarizing oneself with the characteristics of the materials, the pressure range required, and potential environmental factors can aid in selecting a valve that ensures safety and prolongs system longevity.
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting a Pressure Reducing Valve
When selecting a pressure reducing valve (PRV), several key factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance and reliability. One of the primary considerations is the pressure range. According to the Hydraulic Institute, nearly 70% of system failures are linked to improper pressure settings. Therefore, it's crucial to choose a PRV that can handle the specific inlet and outlet pressures of your application. A well-suited PRV will not only maintain the desired downstream pressure but also protect downstream equipment from damage caused by pressure spikes.
Another vital aspect is the valve material and compatibility with the fluid being controlled. The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) reports that material selection impacts valve lifespan and maintenance costs significantly. For instance, when dealing with corrosive fluids, selecting a valve constructed from stainless steel or specially coated materials can prevent premature failure. Additionally, the flow capacity of the valve must match the system's demands; oversizing or undersizing can lead to inefficiencies, as noted in a recent study by the International Society of Automation, which emphasized that accurately sized PRVs can enhance system efficiency by up to 30%. Understanding these factors is essential for making an informed decision that contributes to long-term operational success.
Comparing Types of Pressure Reducing Valves for Specific Needs
When selecting a pressure reducing valve (PRV), it's essential to understand the various types available and how they cater to specific needs. There are generally three main types of PRVs: spring-loaded, pilot-operated, and electronic. Spring-loaded valves are often used for residential applications due to their simplicity and reliability. However, for industrial setups requiring precise control, pilot-operated valves provide better performance and response times. Electronic valves offer advanced features, allowing for integration with automated systems, making them ideal for high-tech environments.
One of the essential tips for choosing the right PRV is to determine the required flow rate and pressure specifications for your application. Knowing these parameters helps in selecting a valve that meets operational demands without causing undue wear or failure. Additionally, consider the material of the valve. Brass and stainless steel are popular choices, with stainless steel offering enhanced durability for corrosive environments.
Lastly, ensure the PRV comes with an adequate warranty and support. This can significantly impact maintenance and repair costs in the long run. Having reliable customer service and support for your specific valve type can ease concerns about any potential operational issues and help maintain your system's efficiency.

Maintenance Tips for Enhancing the Longevity of Pressure Reducing Valves
Proper maintenance is crucial for enhancing the longevity of pressure reducing valves (PRVs). Regular inspections should be conducted to identify any signs of wear, corrosion, or leakage. It is advisable to check the valve’s sealing surfaces and adjust the spring tension, if necessary, to ensure optimal performance. Cleaning the valve periodically prevents debris from accumulating, which can lead to malfunction. Also, using the correct lubricants can significantly enhance the efficiency of the components and reduce friction, thus prolonging the lifespan of the valve.
In addition to inspections and cleaning, ensure that the pressure levels in the system remain within the manufacturer's recommended specifications. Overpressurization can lead to premature wear and failure of the PRV. Keeping a log of maintenance activities allows for tracking the valve's performance over time, identifying potential issues early, and scheduling replacements before any failures occur. Lastly, training staff on proper handling and operation of the system can prevent mishaps that could shorten the life of the pressure reducing valve. With these proactive maintenance tips, users can significantly extend the operational life of their pressure reducing valves, ensuring reliable performance within their systems.
Pressure Reducing Valve Maintenance Tips
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing a Pressure Reducing Valve
When selecting a pressure reducing valve (PRV), avoiding common pitfalls is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. One of the most frequent mistakes is neglecting to consider the flow capacity. According to a 2021 industry report by the Hydraulic Institute, inappropriate sizing can lead to pressure fluctuations, noise, and even premature valve failure. It is essential to select a PRV that is correctly sized for the specific requirements of your system, which means taking both the maximum and minimum flow rates into account.
Another common oversight is failing to account for the media type and temperature. A recent survey by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers indicated that over 30% of system failures were linked to incorrect material selection based on the process media. Different materials exhibit varying resistance to corrosion, wear, and thermal expansion, which can significantly impact the PRV’s lifespan and efficacy. It's vital to choose a valve that not only meets the pressure requirements but also aligns with the chemical and thermal properties of the fluid being controlled to avoid costly breakdowns and repairs.

Related Posts
-

The Essential Guide to Understanding Pressure Relief Valves: Safety and Function Explained
-
Understanding the Importance of Hydraulic Pressure Control Valves in Modern Industrial Applications
-

Why Hydraulic Flow Control Valves are Essential for Optimizing System Performance: Insights and Data
-
Understanding the Role of Hydraulic Valves in Modern Industrial Applications
-
The Future of Automation: How Servo Valves are Revolutionizing Industry Efficiency
-
Understanding Yuken Directional Valves and Their Applications in Modern Hydraulic Systems












